Mr. Yang Fan, Co-founder and Vice President of SenseTime ▎AI brings a new development paradigms and becomes the key to breaking boundaries
In today's era, technology seems to have a certain distance from most people, but it is actually closely related to everyone.
People began to enjoy abundant material life, which started with the Industrial Revolution. The progress and mutation of science and technology had brought about a huge increase in productivity. Later, the world went through the Electrical Revolution and the Information Age successively.
Nevertheless, in the last 40 years, the evolution of the entire human basic science has obviously slowed down.
So, how to achieve new larger-scale and larger-volume scientific and technological breakthroughs, thus further improving productivity and further optimizing production relations?
When looking back in history, we can find that there are different paradigms for innovation. The first paradigm was empirical induction. Through many physical phenomena, experiences were extracted and summarized, or assumptions were proposed and then used as bases to verify experiences.

The second paradigm was reasoning and deduction, or formula deduction in short; based on a theoretical calculation and derivation, some new conclusive results were obtained.
Later, with the advent of the Era of Machine and the Era of Intelligence, there emerged the third paradigm: simulation. Machines took place of humans in reasoning and deduction, and they might be far superior to natural humans in efficiency and capability of deducing formulas - what they needed were only more data and initial conditions.
In recent years, with the upgrading and evolution of big data, the fourth paradigm has emerged. Deep learning is used to let more data be updated through machine experience induction. Although it is not very clear to people why this data can induce such a conclusion, machines can identify it accurately.
Mr. Yang Fan said that other than the so-called first, second, third and fourth paradigms, what really drives us to make a lot of innovations is often beyond induction and beyond reasoning. We call it “brain hole of genius”.
Some people say that Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity is a wisdom beyond the times, or rather, it is a contingency or necessity without foundation at all and without previous system support. With this kind of mutant thinking and innovation, which is similar to the brain hole of genius, machine may be able to do something analogous - “machine conjecture”.
In the past two years, we have seen that “machine conjectures” have made breakthroughs in frontier innovations in some cross-domain disciplines and academic fields.
For example, last year, AlphaFold detected structures of more than 300,000 kinds of proteins, solving the protein sequencing problem that has not been solved by the biological community for more than 50 years; another example is DeepMind, which has realized a controlled nuclear fusion in a simulated environment for the first time by using reinforcement learning.
Nowadays, AI has helped people make key breakthroughs in academic issues that have plagued humans for several decades. It is believable that in the future, AI can help us bring more surprises in more technological fields, including physics, chemistry, astronomy, materials, biology, and medicine.
▎ AI infrastructures: provide important large-scale, high-efficiency and low-cost basic support for AI development
AI has three major elements: computing power, algorithm, and data. In the past ten years, with the industrial application of AI technologies, demands for computing power, data, and model parameter volume have grown exponentially.

Since 2014, the number of parameters of single AI models has increased by 300,000~400,000 times, or doubled every three months, and the growth rate is far faster than that specified by Moore's Law.
In the recent two years, industry giants have invested heavily one after another in building their own AI infrastructures. For example, Meta has built its own AI supercomputer, which will, by this July, hopefully have got more than 16,000 Nvidia A100 GPUs to hit a computer power over 5000 P (Petaflop) (1 P = 1000 trillion times/second, 5000 P = 5,000,000 trillion times/second); in addition, Tesla also officially launched its self-developed supercomputer Dojo last year for the R&D of next-generation autonomous driving technology.
AI has a very clear leverage effect:The economic value created by the AI industry itself can bring 10 times of leverage to the industry it serves and supports.
Or in other words, AI application creates a market of 200 billion yuan, meaning that has brought a growth of 2 trillion yuan to the entire industrial economy and still maintains a very high growth rate.
So, what does AI need for the next stage of development?
Mr. Yang Fan said that as AI develops toward the next stage, it needs a powerful infrastructure,which provides larger-scale, higher-efficiency, and lower-cost basic support for AI’s required three major elements - computing power, algorithm, and data core.With such support, AI applications serving various industries will be rapidly developed and implemented.
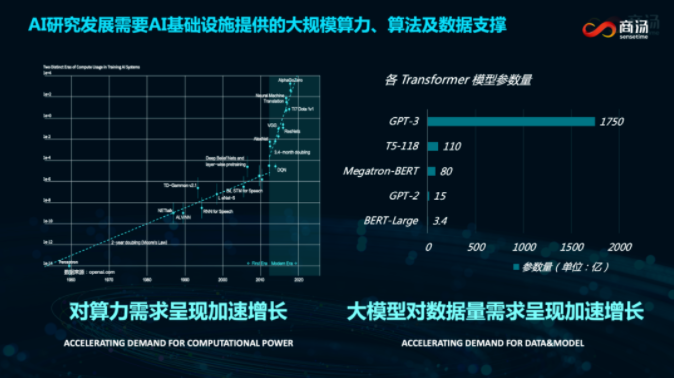
In the aspect of computing power, the computing power required by AI nowadays is totally different from that required by information and cloud services in the past two decades. Traditional cloud services provide computing, but storage accounts for a larger proportion. Just the contrary, computing occupies a far greater proportion than storage in AI infrastructures, which also support various heterogeneous hardware structures and rely more on dedicated hardware and software.
Therefore, what we need more are universal, open, and shared infrastructures.
In terms of algorithms, with the development of AI industry, a large number of high-value application scenarios have emerged, but the costs for AI solve problems are too high, resulting in many scenarios difficult to implement.
The industry evolution follows the direction in which more data are gathered and a larger model is used to support rapid iterations and innovations in long-tail scenario applications, so that costs of single technology innovations will be greatly diluted.
Data plays the role of core fuel to promote technological innovation in the field of AI, and has a non-linear effect: if 10 times of data is put together, various technological capabilities created from it may be 100 times or even more.
Yet, the question is, how to gather a larger volume of data and use it wider? This needs the support of AI infrastructures at the back. Of course, proper data security and privacy protection are also required.
▎ SenseCore: Pave the way required for AI innovations by opening up
As early as 2019, SenseTime started the research and development of SenseCore, an AI infrastructure.
It has a powerful general AI capability, gathers a lot of computing power, algorithms, and data, and solves software and hardware problems from the process in an integrated way, thus forming a strong support system.
SenseCore delivers a computing power as high as 3740P, and is, by far, the largest general AI infrastructure in China. Up to now, it has provided a large number of scientific research institutions and head enterprises in the Yangtze River Delta with core competence services in the whole field of computing power, data, and algorithms, supporting the application of AI in a wide range of industrial fields.
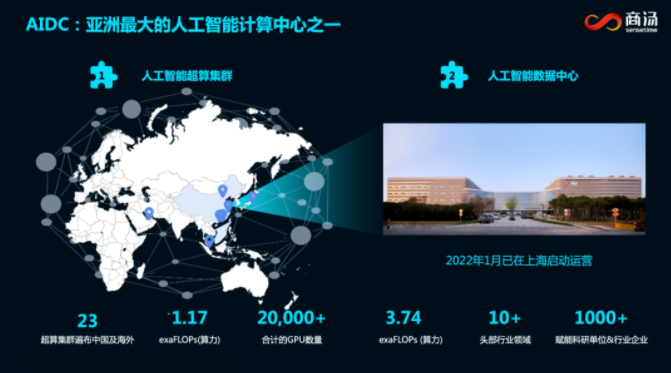
Typically, it covers: protein prediction and basic scientific research innovations in biomedicine; vehicle-road coordination of intelligent traffic, from simulation to planning-prediction integration; and a large number of technological innovations, which support virtual physical engines and virtual intelligent engines…
Mr. Yang Fan said that through the convergence of core infrastructures, we can achieve a larger-scale, higher-efficiency, and low-cost supply of computing power, data, and algorithms, and support better platform opening up. SenseCore will pave the way required for AI innovations by opening up.
In the future, AI, as a very general industry technology, can carry out a lot of innovations regarding assorted application problems faced by different industries, and rapidly drive the development and progress of various industries.